What is the Difference Between Trading and Investing? A Clear Guide
Learn the key differences between trading and investing. This guide explores timeframes, risks, benefits, and which approach is right for you.
 Writen by:
Arslan Ali But
07 January 2025
8 minutes read
Writen by:
Arslan Ali But
07 January 2025
8 minutes read


Trading and investing are two distinct approaches to profiting in the stock market, each with its own strategies, ideologies, and analytical methods. While both aim to grow wealth, their differences lie in how they capitalize on opportunities and the timeframes they operate within.
Without a clear understanding of these financial methods, succeeding in the stock market becomes a challenge. Knowing whether you’re trading or investing is crucial—it directly influences your decisions on when to buy, hold, or sell.
This guide simplifies the fundamentals of both strategies, helping you determine the approach that aligns best with your financial goals. If you're unsure where to begin, WhereToTrade can connect you with brokers tailored to your needs. Let’s dive in to uncover which strategy suits you best and how to navigate the financial markets effectively.
What is Trading in Financial Markets?
Trading in financial markets involves the active buying and selling of assets such as stocks, bonds, commodities, and cryptocurrencies with the primary goal of generating profits. Unlike long-term investing, trading focuses on frequent transactions, often within short timeframes such as days, hours, or even minutes.
For instance, a trader might buy Tesla (TSLA) shares at $700 in the morning, expecting the price to rise due to positive earnings reports. If the price reaches $730 by midday, the trader sells, pocketing a $30 profit per share. This active approach demands constant attention to market movements, news, and technical indicators.

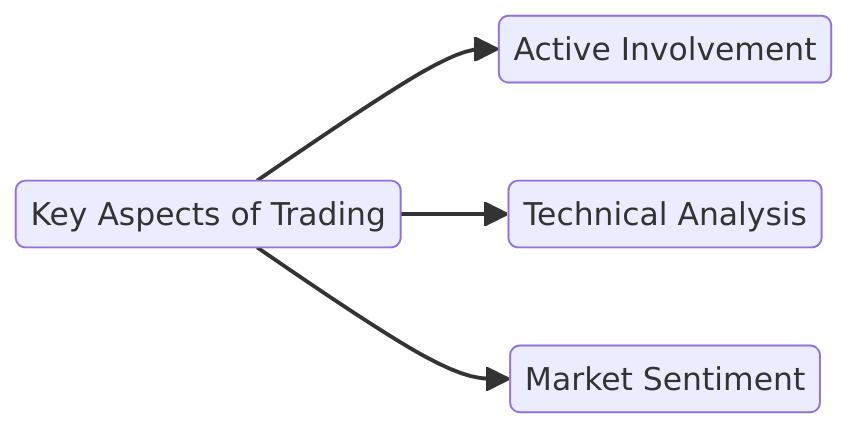
Key Aspects of Trading
- Active Involvement: Traders must stay updated on market news, such as interest rate changes or economic data like the U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP). For example, a strong NFP report might push the USD higher, creating trading opportunities in forex markets.
- Technical Analysis: Charts, patterns, and indicators like Moving Averages and RSI help traders predict price movements.
- Market Sentiment: Understanding how investors react to events, such as geopolitical tensions, can influence trading strategies.
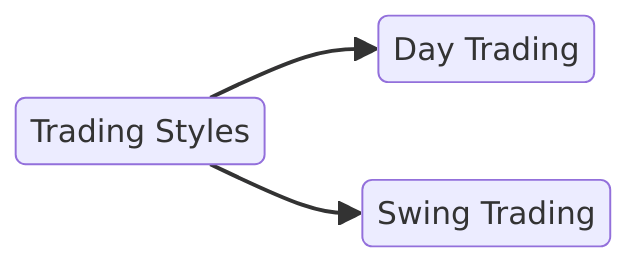
Trading Styles
1. Day Trading
Day trading involves opening and closing trades within the same day to profit from short-term price changes.
Example:
A day trader buys 100 shares of Apple (AAPL) at $150 and sells at $152 within hours, earning a $200 profit.Strategies:
- Trend Following: Riding a stock’s upward or downward momentum.
- Scalping: Making multiple small trades for quick gains, such as earning $0.50 per share on 200 shares multiple times a day.
Requirements:
Day trading demands discipline, technical expertise, and high liquidity assets like NASDAQ stocks or forex pairs like EUR/USD.2. Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days or weeks to capture medium-term trends.
Example:
A swing trader buys Bitcoin at $20,000 during a dip, anticipating a rise due to institutional adoption, and sells it at $25,000 a week later for a $5,000 profit.Strategies:
- Breakout Trading: Buying when a stock price breaks past its resistance level, signaling potential further gains.
- Mean Reversion: Investing in undervalued assets expecting a return to their average price.
- Momentum Trading: Buying assets with strong upward trends and exiting before momentum slows.
What Differentiates Trading?
- Frequency: While investing is about buying and holding, trading is about capitalizing on frequent price fluctuations.
- Risk and Reward: Trading offers higher potential returns but comes with increased risks due to leverage and market volatility.
- Time Commitment: Trading requires active monitoring, while investing often demands patience and a long-term view.
What is Investing?
Investing focuses on long-term growth by buying and holding financial instruments like stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. The aim is to achieve long-term gains by benefiting from asset appreciation, dividends, or interest. For example, an individual retirement account (IRA) invested in a benchmark index like the S&P 500 can provide steady growth over decades to fund goals like retirement or college tuition.
Investors often diversify across asset classes such as real estate, bonds, and other investment instruments to reduce risks and align with their investment objectives. This approach suits those with a higher risk tolerance who aim for stability in volatile markets.
Investing Styles:
- Active Investing: Requires closely monitoring market conditions, buying and selling stocks or other assets to outperform a benchmark index. For instance, active investors might switch sectors based on market trends to maximize returns.
- Passive Investing: A more hands-off approach where passive investors buy and hold investments like ETFs, focusing on long-term performance rather than short-term gains.
Risks Involved:
Investing carries risks like market volatility and falling markets, but its focus on the long haul makes it ideal for long-term investors seeking to generate returns steadily.

To align your investments with your financial goals, platforms like WhereToTrade can connect you with financial advisors who provide personalized investment advice and help create a tailored investment plan.
Key Differences Between Trading and Investing
Understanding the key differences between trading and investing helps you decide which approach aligns with your financial goals. Let’s break it down:
Time Horizon
Trading focuses on short-term gains by capitalizing on price movements within hours, days, or weeks. For example, a day trader might buy Tesla (TSLA) stock in the morning and sell it by the end of the trading day, profiting from small fluctuations in share prices. Investing, on the other hand, takes a longer period—often years or even decades.
For instance, buying an S&P 500 benchmark index fund and holding it in an individual retirement account aims for long-term growth.
Risk Levels
Trading involves higher risks, as it depends on volatile market conditions and requires closely monitoring price swings. A trader focusing on short-term profit during volatile markets might face significant losses if trends reverse unexpectedly. Investing, while not risk-free, carries less risk as it leverages long-term investing to smooth out market volatility and benefit from future results.
Returns
Traders aim for smaller, frequent profits, while long-term investors focus on compounding wealth over time. For example, a trader might earn 2-3% per trade, while an investor holding Apple (AAPL) stock for 10 years could see returns exceeding 200%.
Skill Set
Traders require advanced skills, such as analyzing technical analysis tools like moving averages or stochastic oscillators to identify short-term opportunities. Investors, however, focus on fundamental analysis, like evaluating a company's earnings or industry trends.
Engagement
Trading requires active involvement, often demanding full-time effort to study market conditions and execute trades. Conversely, passive investing involves less frequent action, allowing you to "set it and forget it" while aiming for long-term gains.
Both approaches have their merits, but understanding how much risk you're willing to take and your investment objectives is critical. If you’re still unsure, WhereToTrade can connect you with brokers and tools tailored to your needs, whether you prefer shorter periods for trading or the long haul of investing.
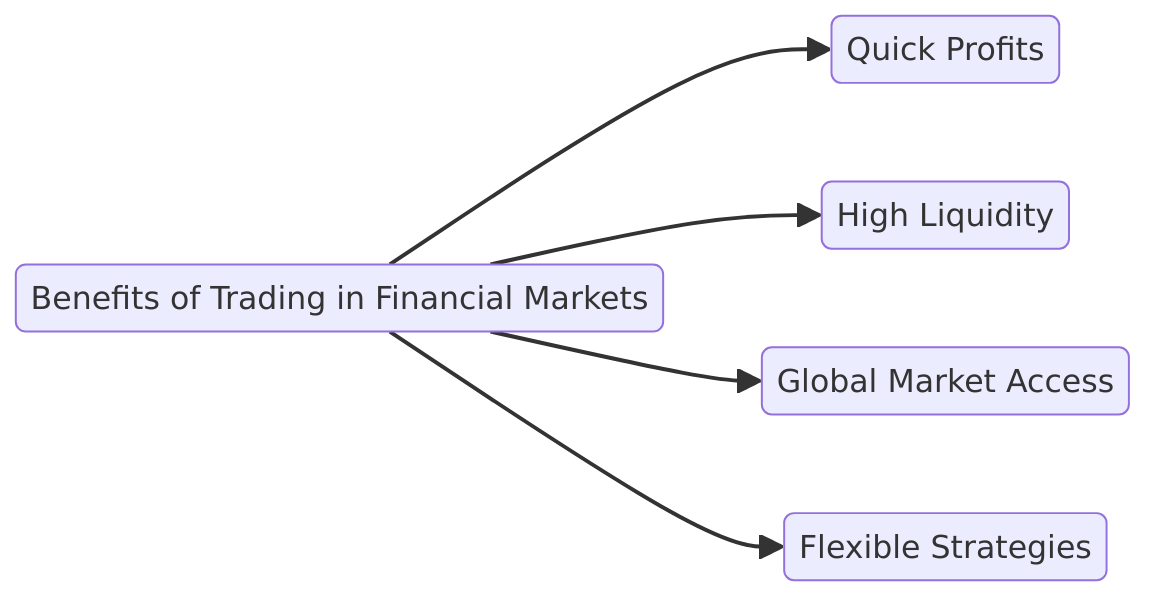
Benefits of Trading in Financial Markets
Trading in financial markets provides several advantages for those aiming to achieve short-term profits and create diversified income streams.
Here's why trading is a compelling choice:
- Quick Profits: Traders can capitalize on intraday price movements. For example, buying Tesla (TSLA) stocks during a morning dip and selling them later in the day could yield immediate gains.
- High Liquidity: Markets like forex and stocks allow assets such as EUR/USD or Apple shares to be bought or sold quickly, ensuring minimal price impact during transactions.
- Global Market Access: Trading opens the door to global opportunities, enabling diversification across asset classes like commodities, stocks, or cryptocurrencies to manage risks during volatile markets.
Flexible Strategies:
- Scalping for rapid trades and quick profits.
- Swing trading to capture medium-term trends.
- Day trading for those closely monitoring price movements.
- For instance, during geopolitical tensions, a swing trader might hold gold, anticipating its rise as a safe-haven asset.
Benefits of Investing in Financial Markets
Investing in financial markets offers a path to long-term financial growth and stability, making it ideal for those with retirement goals or a focus on sustained returns. Here's why investing stands out:
- Power of Compounding: Compounding allows your returns to generate additional earnings. For example, a $10,000 investment growing at an annual rate of 8% could more than double to $21,589 in 10 years, significantly boosting wealth over time.
- Lower Stress Levels: Unlike trading, investing doesn’t require constant monitoring or frequent decisions. By selecting quality assets and holding them, investors can build wealth with less day-to-day involvement.
- Dividends: Some assets, such as individual stocks and mutual funds, pay regular dividends, providing a steady income stream alongside capital appreciation.
Example: Investing in dividend-paying stocks like Coca-Cola (KO) can deliver consistent returns through both share value growth and regular payouts.
Additionally, diversified portfolios with stocks, bonds, and other assets generally show consistent growth over the long haul, even during market volatility. With its focus on long-term gains, investing remains a reliable strategy for achieving financial goals like funding an individual retirement account or a child’s college tuition.
Risks of Trading vs. Investing: Aligning Risk Tolerance
Trading Risks: Navigating Volatile Markets
Trading, while offering the potential for quick profits, comes with higher risks due to its nature. Traders hold assets for shorter periods and often deal with highly volatile financial instruments like options or futures contracts. These assets, coupled with leverage or margin trading, can amplify gains but also significantly increase the likelihood of losses.
For example, a trader using leverage to buy Bitcoin (BTC) at $50,000 could see substantial profits if it rises to $55,000. However, a sudden dip to $48,000 might trigger a margin call, wiping out their initial investment.
The reliance on technical analysis tools like moving averages or stochastic oscillators is crucial but also requires consistent market monitoring and quick decision-making.
Investing Risks: Long-Term Stability with Fluctuations
Investing focuses on building wealth over time but isn’t without risks. Economic downturns, such as the 2008 financial crisis, can drastically reduce the value of investment instruments like stocks or mutual funds. Additionally, poor company performance—e.g., declining revenues or management issues—can negatively impact stock values.
Certain asset classes, like real estate or small-cap stocks, may also face liquidity issues, making them harder to sell during market downturns. For instance, during the 2020 pandemic, many real estate investors found it challenging to offload properties due to reduced demand.
Which Approach Suits Your Financial Goals?
Your decision to trade or invest should align with your risk tolerance, time availability, and financial objectives:
- Trading: Best for individuals who can closely monitor markets and use tools like technical analysis to make quick decisions.
- Investing: Suitable for those looking for long-term gains, such as building a retirement fund or saving for college tuition.
Balanced Strategy Example: A professional with a busy schedule might allocate 80% of their portfolio to long-term assets like mutual funds while using 20% for swing trading in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies, combining long-term growth with occasional short-term profits.
Conclusion: Trading or Investing—The Choice Is Yours
When considering trading and investing, evaluate your financial situation, goals, and how much risk you’re willing to take. Whether you’re planning for the long haul or aiming for short-term gains, understanding the key differences and aligning them with your strategy is vital.
Start by building a well-rounded investment plan that incorporates both strategies. With the right approach and informed decisions, you can achieve long-term financial stability while exploring market opportunities.
If you’re unsure about where to start or which broker aligns with your needs, WhereToTrade is here to help. Explore WhereToTrade today or consult with an expert to make informed decisions and take the next step in your trading journey.
Table of contents
1. What is Trading in Financial Markets? 2. What is Investing? 3. Key Differences Between Trading and Investing 4. Here's why trading is a compelling choice 5. Benefits of Investing in Financial Markets 6. Risks of Trading vs. Investing: Aligning Risk Tolerance 7. Which Approach Suits Your Financial Goals? 8. Conclusion






