What Are CFDs?
Discover Contracts for Difference (CFDs), a versatile trading tool that allows you to speculate on price movements of assets like stocks, commodities, and currencies without owning them. Learn how they work, their benefits, and the risks involved.
 Writen by:
Arslan Ali But
07 January 2025
8 minutes read
Writen by:
Arslan Ali But
07 January 2025
8 minutes read

Contracts for Difference (CFDs) are innovative financial instruments that allow traders to speculate on the price movements of various assets, such as stocks, commodities, forex, and cryptocurrencies, without owning the underlying asset. CFDs are agreements between a trader and a broker to exchange the difference in an asset's price between the time a trade is opened and closed.
This flexibility has made CFDs a popular choice among traders, offering the opportunity to profit from rising or falling markets. Using leverage, traders can control larger positions with relatively small capital. However, the same leverage that enhances profit potential also increases risk, making effective risk management essential.
This article delves into how CFDs work, their advantages, and the potential challenges they pose, helping you decide if they align with your trading goals.
What Are CFDs?
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) are financial derivatives that allow traders to profit from asset price movements without owning the underlying asset. Traders enter agreements with brokers to exchange the difference in an asset’s value from the opening to closing of a trade.
For instance:
- A trader expecting gold prices to rise buys a gold CFD.
- Another trader predicting a decline might short-sell the CFD.
This flexibility allows traders to access diverse markets, including equities, indices, commodities, and cryptocurrencies, all through a single online platform. CFDs have become a popular choice for traders seeking to capitalize on global opportunities efficiently.
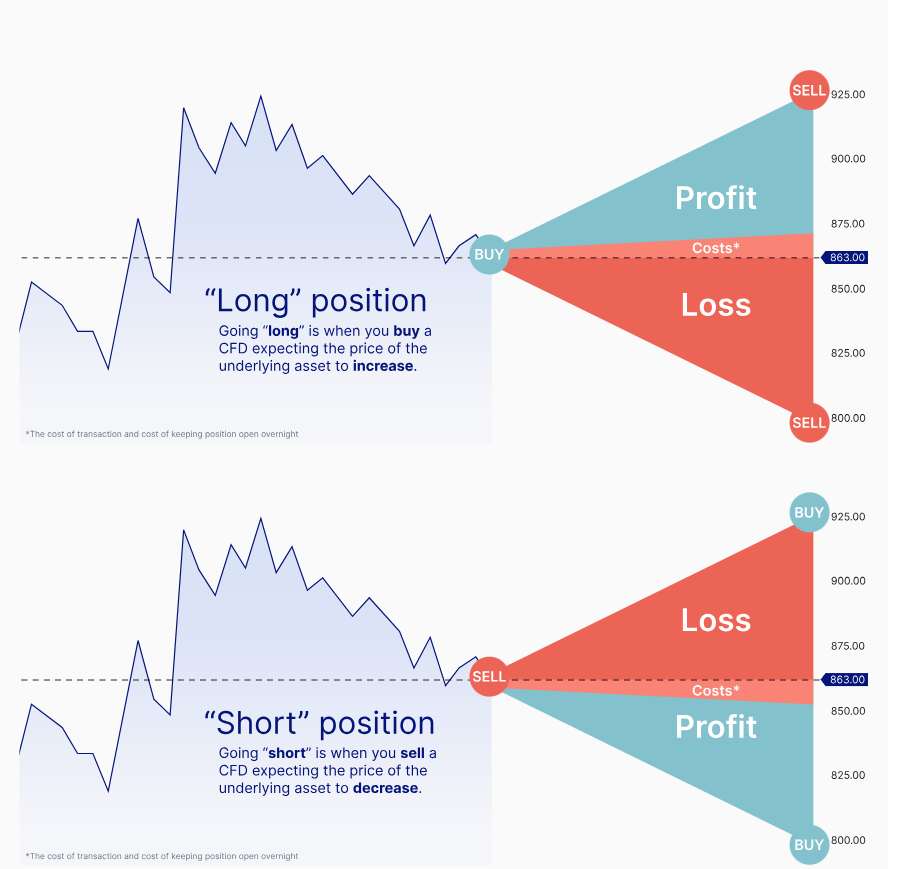
How CFDs Work
CFDs allow traders to speculate on asset price movements without owning the underlying asset, making them versatile tools in modern trading.
Long Positions: Traders buy CFDs expecting prices to rise, intending to sell them at a higher price.
Short Positions:Traders sell CFDs anticipating prices to fall, aiming to repurchase at a lower price.
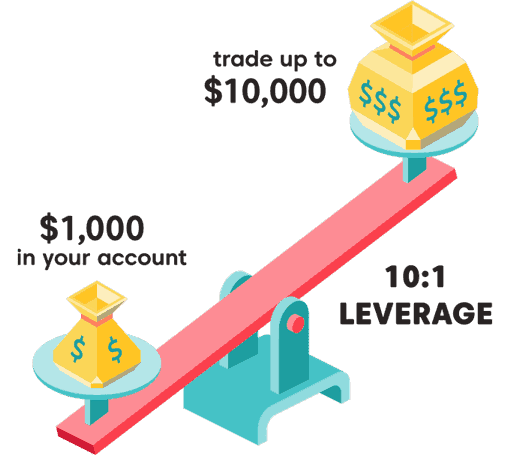
Leverage and Risk:
Leverage is a defining feature of CFDs, enabling traders to control significant market exposure with a fraction of the required capital (margin).
Example:
- With 10:1 leverage, a trader can control a $10,000 position with just $1,000. A 1% market move results in a 10% gain or loss on the trader’s capital.
- This amplified potential makes CFDs appealing, but it also heightens risks, especially during volatile market conditions. Coupled with no fixed expiration dates, CFDs offer unparalleled flexibility but demand disciplined risk management.
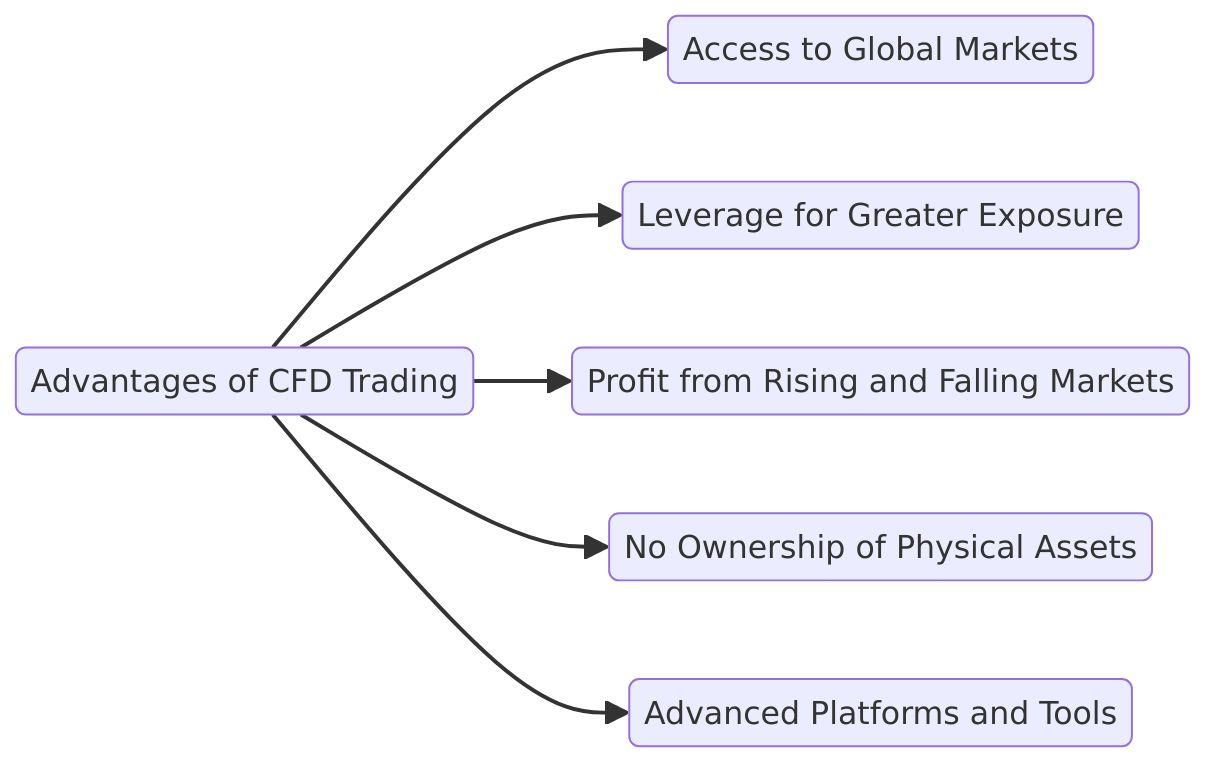
Advantages of CFD Trading
CFDs have become a go-to choice for traders due to their flexibility, accessibility, and diverse opportunities. Here’s why they stand out:
1. Access to Global Markets
CFDs provide exposure to multiple asset classes, from commodities to cryptocurrencies, through a single platform.
Example: Brokers like eToro and AvaTrade offer access to over 2,000 CFDs, enabling portfolio diversification.
2. Leverage for Greater Exposure
CFDs enable traders to amplify exposure with less capital.
Example: With 20:1 leverage, controlling a $20,000 position requires just $1,000, making CFDs attractive for traders seeking high returns.
3. Profit from Rising and Falling Markets
CFDs allow traders to benefit from both market directions:
- Going long in bullish markets.
- Short-selling in bearish conditions.
4. No Ownership of Physical Assets
Trading CFDs eliminates the complexities of storing or delivering physical assets.
5. Advanced Platforms and Tools
CFD platforms provide real-time data, charting tools, and user-friendly interfaces, simplifying trading for both beginners and seasoned professionals.
Risks of CFD Trading
While CFDs offer unique opportunities, they also come with significant risks that traders need to manage effectively:
1. Leverage: A Double-Edged Sword
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with smaller capital, but it can amplify losses just as easily as gains.
Example: A 10x leveraged trade means a 1% market drop results in a 10% loss on the trader’s capital. Without careful risk management, losses can quickly spiral out of control, even exceeding the initial deposit.
2. Market Volatility
CFDs are highly sensitive to price movements, making them vulnerable to sudden market fluctuations. Unexpected events, such as geopolitical tensions or economic data releases, can lead to rapid losses.
Stat: In 2023, crude oil CFDs saw intraday price swings exceeding 15% during OPEC announcements, underlining the importance of vigilance in volatile markets.
3. Fees and Spreads
Trading CFDs incurs costs like spreads, commissions, and overnight holding fees. These expenses can erode profits over time, especially for active traders.
Example: Holding a position overnight in forex CFDs can attract a swap fee that eats into potential gains, emphasizing the need to factor in trading costs.
4. Risk of Losing More Than Deposits
Highly leveraged positions can result in losses exceeding the initial investment. Without protective measures like stop-loss orders, traders face the risk of substantial financial damage.
5. Counterparty Risk
In unregulated markets, traders face the risk of brokers failing to honor payouts or meet obligations. It’s critical to trade with regulated brokers to mitigate this risk.
CFDs are not suitable for everyone, especially inexperienced traders. Before diving in, ensure you have a robust strategy, thorough market knowledge, and effective risk management practices in place.
CFDs vs. Other Trading Instruments
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) offer unique advantages compared to traditional instruments like options, futures, and spot trading. Here's how they differ, with relevant data to highlight their significance:
1. No Ownership of Assets
CFDs allow traders to speculate on price movements without owning the underlying asset, enabling profit opportunities in both rising and falling markets.
Example: In 2024, the average gold CFD trader saw a 12% increase in profitability during volatile markets, leveraging short-selling opportunities without the need for physical gold storage or delivery.
2. Flexibility Over Options and Futures
Unlike futures or options, which have fixed expiration dates and complex pricing models, CFDs provide flexibility to open or close positions at any time.
Stat: Futures trading often requires a minimum contract value of $50,000, while CFD trading allows positions starting from $1,000 with a 10:1 leverage ratio, making them accessible to a broader audience.
3. Leverage and Accessibility
CFDs use leverage, allowing traders to amplify market exposure with limited capital. For instance, a trader with $1,000 can control a $10,000 position using 10:1 leverage.
Warning: While leverage amplifies profits, 76% of retail CFD accounts lose money due to improper risk management and volatile markets, according to industry reports.
CFDs simplify market access but require caution, balancing flexibility with the risks inherent in leverage.
Getting Started with CFDs
Starting with CFDs requires preparation and a strategic approach. Here’s how to begin effectively:
Choose a Reliable Broker
Select a broker that offers a broad range of assets, competitive spreads, and is regulated by reputable authorities like the FCA (UK) or ASIC (Australia). Ensure the platform provides robust tools for analysis and trading.
Practice on Demo Accounts
Use demo accounts to familiarize yourself with the trading platform and test your strategies without financial risk. Spending adequate time on a demo account helps you understand market dynamics and refine your approach before transitioning to live trading.
Implement Risk Management Strategies
Set clear stop-loss and take-profit orders for every trade to manage potential losses and secure profits. A common guideline is to limit risk to a small percentage of your trading capital per position. For instance, if you have $5,000 in your account, you might cap risk at $100 per trade. This disciplined approach helps protect your capital from significant losses.
By gaining platform expertise, practicing with a demo account, and employing sound risk management strategies, traders can build a strong foundation for navigating the dynamic world of CFDs with confidence.
Conclusion
CFDs are a flexible and accessible way to trade global markets, offering opportunities to profit from both rising and falling prices. With the ability to trade using leverage and access diverse assets like stocks, commodities, and forex, CFDs cater to a wide range of trading strategies.
However, their reliance on leverage makes risk management essential. With data showing that 76% of retail CFD accounts lose money, traders must approach this instrument with discipline, effective strategies, and the right tools.
Choose brokers with transparent pricing, robust platforms, and regulatory oversight. By practicing with demo accounts and adhering to sound risk management principles, CFDs can become a powerful component of your trading portfolio.
Table of contents
1. What Are CFDs? 2. How CFDs Work 3. Advantages of CFD Trading 4. Risks of CFD Trading 5. CFDs vs. Other Trading Instruments 7. Conclusion






